Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) Staging in Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) with UBIX for Increased Reliability
About
Summary
An algorithm for AMD classification with Uncertainty-Based Instance eXclusion (UBIX) for increased reliability.
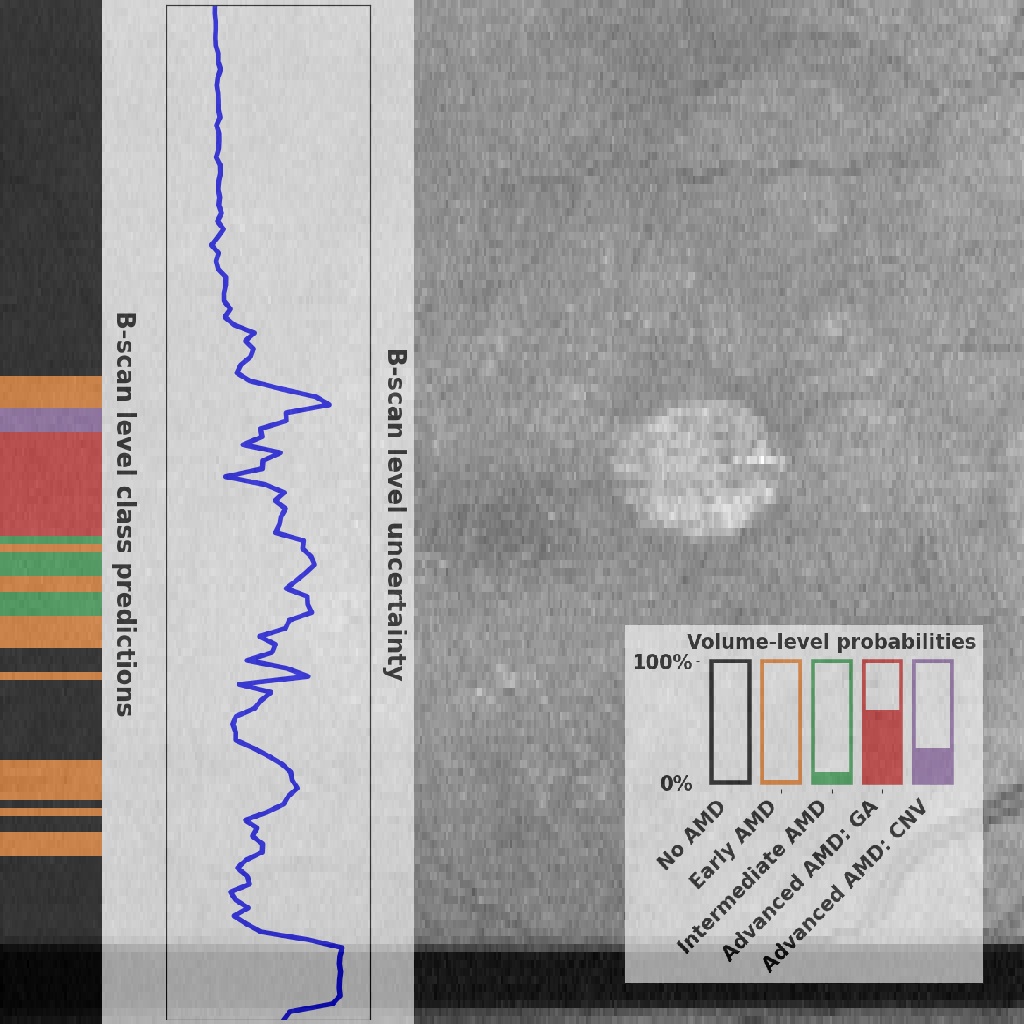
The thumbnail (see example above or on the Results page) show the enface image overlayed with several algorithm results. The banner on the left shows the model predictions on B-scan level. The colors correspond to the same AMD stages as in the probability plot on the bottom right. Next to that, the uncertainty on B-scan level is shown. The bar plot on the bottom right show the volume-level probabilities for each AMD stage.
The table (visible when clicking in the Results column on the Results page or on the left side when in the viewer) shows:
-
"Volume-level classification": The final AMD staging of the full OCT volume (one of No AMD, Early AMD, Intermediate AMD, Advanced AMD: GA, Advanced AMD: CNV)
-
"Volume-level class probabilities": The probability for each final AMD staging of the full OCT volume
- "Volume-level uncertainty": A level of uncertainty that the model gives about the classification that it generated. The lower this number, the more certain the algorithm is. See the publication for the definition of the uncertainty measure used (ordinal entropy). Here, the percentile for this uncertainty (determined using the external Topcon set) is shown as well. It also shows a classification of that uncertainty measure, ranging from "very low" to "very high". A histogram of all volume-level uncertainties on the external Topcon set with the definitions indicated with colors is shown here:

Mechanism
👥 Target population¶
The algorithm has been trained on data from the EUGENDA study, which was acquired in Western Europe.
🕹 Algorithm description¶
A multiple-instance learning classification model with UBIX, which reduces the effect of corrupted instances on the bag-classification by integrating an out-of-distribution (OOD) instance detection technique during inference.
💾 I/O¶
Input: SD-OCT image, full volume.
Output: AMD grading according to the CIRCL grading.
📸 Scanner compatibility¶
The algorithm was trained on Heidelberg Spectralis data, but also evaluated on Topcon and Bioptigen data.
Interfaces
This algorithm implements all of the following input-output combinations:
| Inputs | Outputs | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
Validation and Performance
| Quadratic-weighted kappa | AUC (offset at intermediate AMD) | |
|---|---|---|
| Heidelberg Spectralis (internal, n=680) |
0.861 ± 0.014 | 0.977 ± 0.005 |
| Topcon (external, n=1184) |
0.643 ± 0.036 | 0.810 ± 0.018 |
| Topcon, only blinking artifacts (external, n=33) |
0.708 ± 0.184 | 0.873 ± 0.093 |
| Bioptigen (external, n=384) |
0.783 ± 0.034 | 0.922 ± 0.020 |
Uses and Directions
This algorithm was developed for research purposes only.
Warnings
Some difficult B-scans may potentially picked up by the model as out-of-distribution. Be especially wary of B-scans that are assigned a high uncertainty and check whether this is actually due to an artifact or some other feature that is not related to AMD severity.


